Introduction
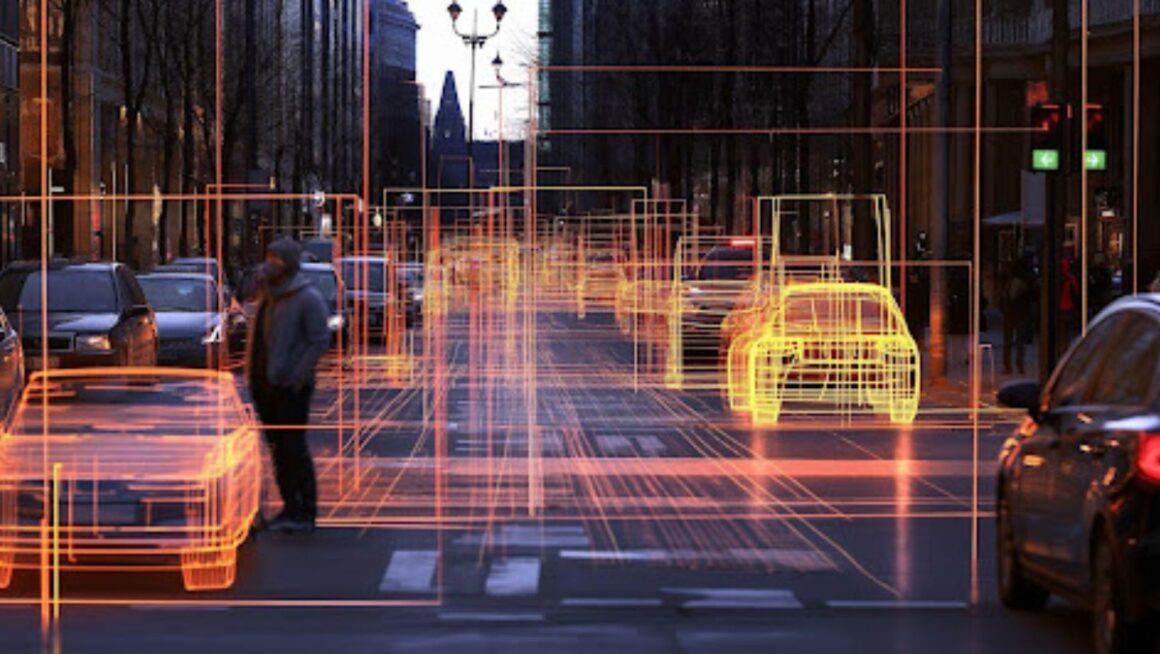
Modern cities are evolving fast, embracing digital transformation to solve urban challenges. Integrating computer vision in traffic and parking management is one of the most exciting advancements. At the heart of this technology is the ability to recognize the car license plate, turning ordinary cameras into intelligent tools that improve traffic flow, enhance safety, and optimize parking. In this article, we’ll explore how computer vision is shaping the future of smart cities and why it’s becoming a must-have technology for modern urban environments.
From traffic optimization to parking automation, computer vision is powering smarter and greener urban mobility systems. As cities grow, they need scalable solutions to manage millions of daily vehicle movements — and that’s where computer vision delivers real value.
What Is Computer Vision and How Does It Power Smart Cities?
Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables machines to interpret and understand visual data from the world, much like humans do. In smart cities, this technology is deployed through a network of connected cameras and sensors to monitor and analyze vast amounts of real-time video and image data.
These intelligent systems can perform complex tasks such as identifying vehicles, analyzing traffic patterns, detecting accidents, and using data from a car license plate dataset to automate parking, tolling, and law enforcement. All of this is done continuously and at scale, providing city authorities with actionable data and real-time decision-making tools.
The power of computer vision lies in its versatility. It can adapt to changing conditions — day or night, rain or shine — and works across diverse environments, from bustling downtown areas to suburban streets. This flexibility is key to making urban mobility systems more adaptive, responsive, and sustainable.
Furthermore, when combined with other smart technologies such as IoT sensors, 5G networks, and cloud computing, computer vision becomes part of an integrated ecosystem for intelligent transportation management.
Applications of Computer Vision in Smart City Traffic
Real-Time Traffic Monitoring and Control
One of the primary applications of computer vision in smart cities is real-time traffic monitoring. AI-powered traffic cameras can perform:
- Vehicle counting
Counting the number of vehicles passing through intersections or highway segments to assess traffic volume and trends.
- Traffic flow analysis
Monitoring vehicle movement patterns to optimize road usage and identify congestion hotspots. - Speed detection
Measuring vehicle speeds to enforce speed limits and promote road safety. - Congestion detection and dynamic signal control
Adjusting traffic light timing dynamically based on current traffic conditions improves flow and minimizes delays.
Cities like Barcelona and Singapore have successfully deployed adaptive traffic signal systems based on computer vision data, achieving measurable reductions in congestion and travel time. These systems also help reduce emissions by minimizing vehicles’ time idling at intersections.
Automated Incident Detection
Another critical use of computer vision is automated incident detection. AI-enabled cameras can:
- Identify accidents, stalled vehicles, and unauthorized maneuvers in real-time.
- Trigger automated alerts to emergency services for faster response.
- Reduce incident response time and improve overall traffic safety.
For example, London’s smart CCTV traffic network has significantly improved emergency response times through real-time AI-based incident detection. Additionally, automated systems help mitigate the risk of secondary accidents by providing timely alerts to both drivers and first responders.
Smart Public Transport Optimization
Computer vision also plays a vital role in optimizing public transportation systems:
- Monitoring bus lane usage and transit priority enforcement
Ensuring that dedicated lanes are used correctly and that buses can maintain schedule reliability. - Passenger counting on buses/trains using AI vision
Providing accurate passenger load data for better fleet management and route planning. - Dynamic route adjustments based on congestion data
Helping transit authorities adjust routes and schedules in response to changing traffic conditions.
This level of optimization leads to more efficient and attractive public transport, helping cities promote sustainable mobility. In the long term, these improvements contribute to reduced car dependency, cleaner air, and lower carbon footprints.
Enhanced Pedestrian and Cyclist Safety
Computer vision technologies contribute significantly to the safety of vulnerable road users:
- Detecting pedestrians and cyclists in intersections and crosswalks.
- Predicting pedestrian crossings to enable proactive responses from vehicles and traffic signals.
- Adaptive lighting and crosswalk signals that adjust based on pedestrian presence and traffic patterns.
Such systems are helping to reduce pedestrian and cyclist injuries in leading smart cities worldwide. For example, some cities are deploying AI-based adaptive lighting that brightens crosswalks as pedestrians approach, improving visibility and safety at night.
Computer Vision for Smart Parking Systems
Smart parking is another vital area where computer vision is transforming city infrastructure. As urban populations grow, demand for efficient parking solutions is increasing.
License Plate Recognition (LPR)
License Plate Recognition (LPR) is at the core of modern smart parking systems. Cameras equipped with computer vision can read the car license plate of any vehicle entering or leaving parking areas.
- Role of car license plate recognition in smart parking and access control
LPR enables seamless parking entry and exit without physical tickets or barriers, improving user experience and operational efficiency. - How AI-enhanced car license plate recognition works
High-resolution cameras capture the car license plate, and AI algorithms process the image to accurately identify the vehicle. This data is then integrated with payment systems or access control platforms.
Automated Parking Guidance
Computer vision can also guide drivers to available parking spaces:
- Real-time parking space availability detection
Cameras continuously monitor parking lots or street parking spots to detect open spaces. - Dynamic digital signage for parking guidance
Drivers are directed to available parking spots via signage or mobile apps, reducing search time and congestion.
Furthermore, smart parking guidance can also integrate with navigation apps, providing drivers with live updates on parking availability before they even arrive at their destination. This helps reduce unnecessary circling and improves overall traffic flow.
Parking Violation Enforcement
Computer vision-based systems enable automated parking enforcement:
- Illegal parking detection
Cameras identify vehicles parked in restricted zones.
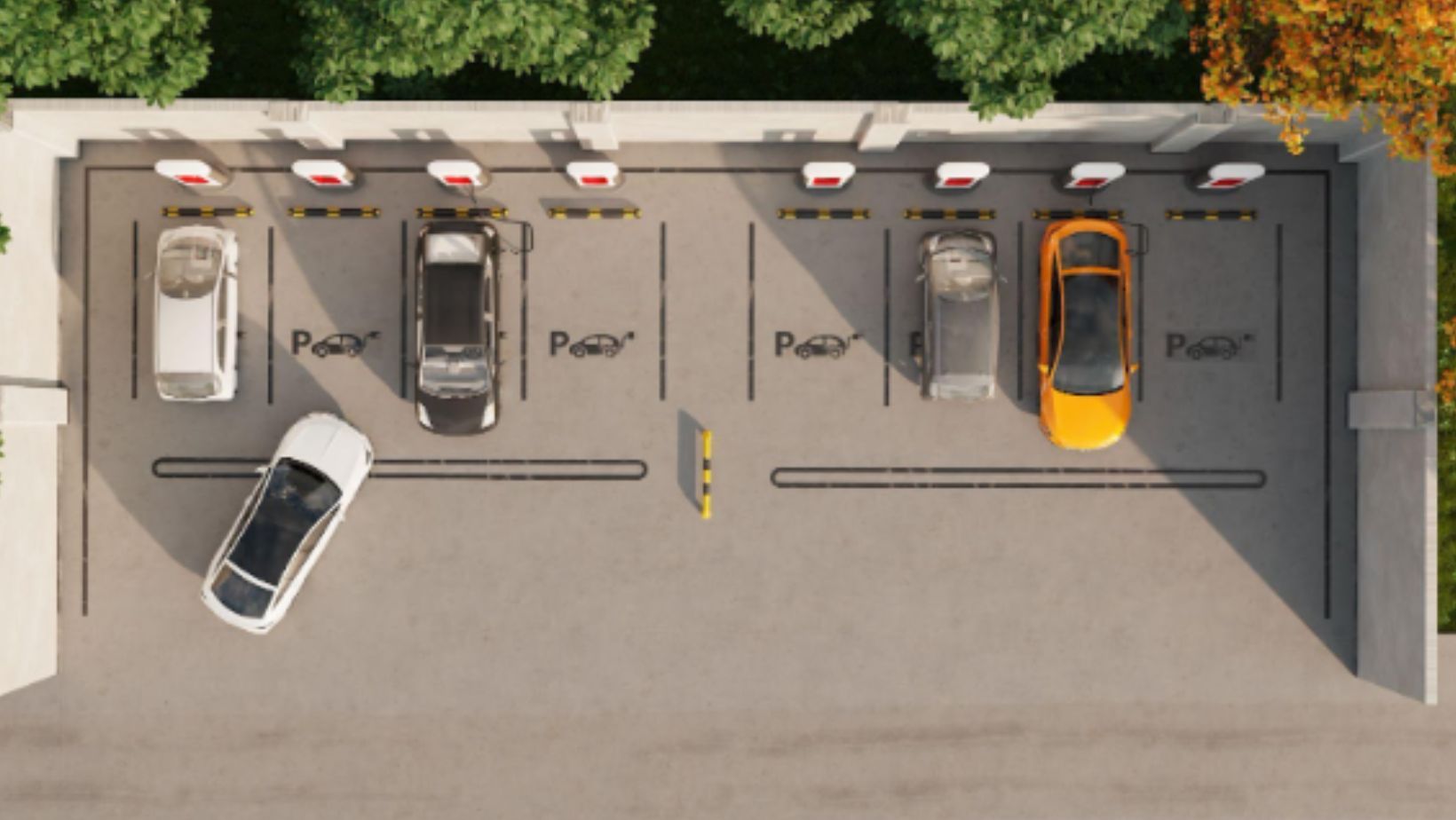

- Unauthorized use of reserved spaces
AI detects violations such as improper use of EV charging spots or handicapped spaces.
Real-time violation detection improves enforcement efficiency and compliance while reducing the need for manual patrols. Many cities now issue electronic citations automatically, streamlining parking management and improving revenue collection.
Benefits of Using Computer Vision in Smart City Traffic and Parking
The integration of computer vision in traffic and parking brings numerous advantages:
| Benefit | Description |
| Improved traffic flow and reduced congestion | Adaptive signal control and smart routing ease traffic bottlenecks. |
| Enhanced road safety and faster emergency response | Automated incident detection enables quicker emergency responses and prevents secondary crashes. |
| Data-driven urban planning and policy-making | Authorities can analyze traffic and parking trends to guide smarter infrastructure investments. |
| Lower emissions through optimized traffic and reduced idle time | Efficient traffic management reduces unnecessary idling, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Increased revenue from smart parking enforcement | Automated enforcement improves compliance and boosts parking revenue. |
| Better user experience for residents and visitors | Smart parking guidance, safer streets, and faster commutes enhance overall urban livability. According to a report by McKinsey & Company, smart mobility solutions can cut commuting times by 15–20% in major cities. |
Conclusion
As cities face increasing challenges from population growth and urbanization, computer vision offers powerful tools to manage transportation systems more intelligently. From car license plate recognition to real-time traffic monitoring, computer vision is driving the next wave of innovation in urban mobility.
Looking ahead, the future of smart cities will increasingly rely on AI-powered vision systems. As the technology evolves, we can expect greater integration with autonomous vehicles, connected infrastructure, and real-time multimodal transport management. This will lead to cities that are not only more efficient and sustainable but also safer and more enjoyable places to live and work.